Events like the recent Construction Safety Week in May and National Safety Month in June are an annual opportunity for people, companies and even competitors to work together and celebrate the incredibly hard work done by people in our industry who make safety the foundation of everything they do and demonstrate their continued commitment to building a stronger, safer industry.
Innovating construction safety involves implementing new ideas, technologies, processes, and practices to reduce risks, prevent accidents, and promote a culture of safety across the construction industry. At JT Magen & Company Inc. we already implement many steps to innovate our construction safety and offer the following recommendations:
- Risk Assessment and Management: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential hazards and vulnerabilities on construction sites. Use tools such as Job Safety Analysis (JSA) and Pre-Shift Meetings to systematically evaluate risks and develop mitigation strategies.
- Training and Education: Invest in ongoing safety training and education programs for workers at all levels, including managers, supervisors, and subcontractors. Provide hands-on training, workshops, and certification courses to ensure that employees have the knowledge and skills to work safely and effectively. The upcoming Safety Week 2024 is an excellent example of this.
- Safety Culture and Leadership: Foster a culture of safety where all employees feel empowered to speak up about safety concerns, report hazards or incidents, and participate in safety initiatives. Lead by example and demonstrate a commitment to safety at all levels of the organization.
- Technological Solutions: Embrace emerging technologies such as wearable devices, drones, and AI-powered analytics to improve safety monitoring, hazard detection, and incident prevention on construction sites. Implement digital tools and platforms for safety management, communication, and reporting.
- Collaborative Planning and Design: Involve safety professionals, architects, engineers, and contractors in the early stages of project planning and design to integrate safety considerations into the project lifecycle. Use Building Information Modeling (BIM) and collaborative design tools to visualize safety hazards and optimize safety measures.
- Prefabrication and Modular Construction: Explore prefabricated and modular construction methods that reduce the need for on-site work and minimize exposure to safety risks. Off-site fabrication allows for controlled environments, standardized processes, and quality control measures that enhance safety.
- Regular Inspections and Audits: Conduct regular safety inspections, audits, and walkthroughs to identify compliance issues, unsafe practices, and potential hazards on construction sites. Implement corrective actions and follow-up measures to address findings promptly.
- Communication and Collaboration: Improve communication and collaboration among project stakeholders, subcontractors, and regulatory authorities to ensure alignment on safety standards, requirements, and best practices. Use digital communication tools, meetings, and safety briefings to keep everyone informed and engaged.
- Continuous Improvement: Establish a system for collecting feedback, analyzing safety data, and implementing continuous improvement initiatives. Encourage workers to provide suggestions for safety enhancements and recognize and reward positive safety behaviors.
- Regulatory Compliance and Standards: Stay informed about relevant safety regulations, codes, and industry standards governing construction operations. Ensure compliance with local, state, and federal safety requirements and proactively address any changes or updates.
By taking a proactive and multidimensional approach to construction safety innovation, we aim to create safer work environments, promote a strong culture of safety, reduce accidents and injuries, and improve overall productivity and project outcomes.
Emerging technologies have the potential to significantly improve workplace safety in the construction industry by providing better risk assessment, enhanced communication, and real-time monitoring of workers and environments. By leveraging these emerging technologies, construction companies like JT Magen & Company can create safer working environments, reduce accidents and injuries, and improve overall productivity and efficiency in the industry.
Here some examples of technologies we strive to develop and improve, and how these technologies can contribute:
- Wearable Technology: Wearable devices such as smart helmets, vests, and wristbands equipped with sensors can monitor vital signs, detect hazardous substances, and provide real-time alerts in case of accidents or dangerous conditions. These devices can also track workers' movements to prevent collisions and ensure they stay within safe zones.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies can be used for immersive safety training simulations, allowing workers to practice handling hazardous situations in a controlled environment. AR can also provide on-site guidance and visual overlays of safety protocols, equipment instructions, and hazard warnings, improving situational awareness.
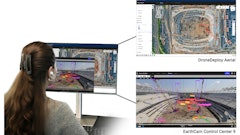
- Drones: Drones equipped with cameras and sensors can conduct aerial surveys of construction sites to identify potential hazards, monitor progress, and inspect hard-to-reach areas without risking worker safety. They can also be used for inventory management and security monitoring.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data from sensors, cameras, and other sources to predict safety incidents, such as falls or equipment malfunctions, before they occur. AI can also optimize resource allocation, schedule maintenance tasks, and automate safety inspections to minimize risks.
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM software enables architects, engineers, and construction teams to create digital models of buildings and infrastructure projects. These models can simulate construction processes, identify safety hazards, and plan logistics more efficiently, reducing the likelihood of accidents during the construction phase. While already in use, the expansion of this technology can only improve our safety profile.
- Robotics and Automation: Robotic systems can perform repetitive or dangerous tasks, such as heavy lifting, demolition, and welding, with precision and consistency, minimizing the need for human intervention in hazardous environments. Collaborative robots (cobots) can work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and safety.
- 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technology allows for the fabrication of complex structures and components with high precision. It can be used to create custom safety equipment, tools, and building materials tailored to specific project requirements, enhancing worker safety and efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics: By applying predictive analytics to historical safety data, construction companies can identify trends, patterns, and risk factors associated with workplace accidents and near-misses. This information can be used to develop proactive safety measures and targeted interventions to prevent future incidents.
- Autonomous Vehicles and Equipment: Autonomous vehicles (AVs) and robotic construction equipment can perform tasks such as material transport, excavation, and site preparation with minimal human intervention. These technologies reduce the risk of accidents caused by human error and improve overall construction site safety.
- Remote Monitoring and Telepresence: Remote monitoring systems and telepresence technologies enable supervisors and safety managers to oversee construction activities and provide real-time guidance to workers from a centralized location. This capability enhances communication, facilitates quick decision-making, and ensures adherence to safety protocols.
- Environmental Monitoring and Control: Advanced environmental monitoring systems can measure air quality, noise levels, temperature, humidity, and other factors that affect worker health and safety. By continuously monitoring and controlling these environmental parameters, construction companies can create safer and more comfortable work environments.
- Exoskeletons: Exoskeletons are wearable robotic devices designed to augment human strength and endurance. They can help reduce the risk of musculoskeletal injuries by providing support and assistance to workers when performing physically demanding tasks such as lifting heavy objects or working in awkward positions.
Events like Construction Safety Week and National Safety Month remind us that at all times, safety is priority No. 1 for our industry, and that it’s our responsibility to follow, expand and enhance safety procedures every day.